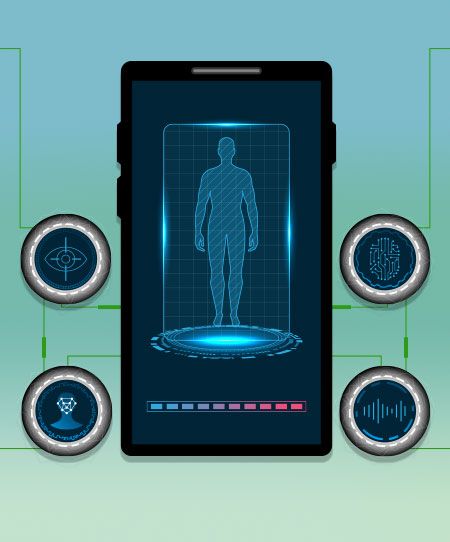
Biometrics is the measurement and analysis of people’s physical characteristics. Since biometric data, such as fingerprints, faces, and irises, are relatively unchanging and unique to each individual, they represent a stronger method for security and user authentication than more traditional data protections. When someone seeks access to a system protected by a biometric security device, their characteristics are compared to their biometric “template” to determine resemblance and grant access. Whereas encryptions and passwords can be overcome by cyber criminals with practice, time, and patience, the uniqueness of biometric data is considerably more difficult for bad actors to fabricate.
Biometric Security is Being Applied Every Day
According to information published by Statista, global biometric systems earned roughly $21.8 billion in revenue in 2018, while mobile biometric technologies brought in a little more than $20 billion. As biometric security technology has developed, it has expanded from primarily criminal identification to a wide range of everyday tasks.
One ideal application for biometric security technology is the healthcare industry. Innovations in the Internet of Things (IoT) have made way for the development of Electronic Health Records (EHR), which are real-time, cloud-based versions of a patient’s medical history. EHRs enable doctors to update a patient’s records and share them with specialists, pharmacies, and other necessary healthcare professionals. Not only do EHRs keep everyone on the same page in regards to a patient’s status, but they also provide the tools to more effectively manage ongoing treatment.
Due to the increase in healthcare information exchanges, and the demand for technology that decreases data corruption and fraud, Grand View Research estimates that the healthcare biometrics market will be worth $14.5 billion by 2025.
The Healthcare Information that Biometrics Data Can Protect
The healthcare industry is investing in biometrics to accurately identify both patients and clinicians. Healthcare organizations generally use two-factor or multi-factor biometric authentication and single sign-in for staff and patient identification. While its first goal is to restrict access to patients’ EHRs and other private health information, biometrics also enable the healthcare industry to secure its most high-risk workflows.
For example, electronic prescriptions for controlled substances are a key target for cyber criminals to penetrate. As a result, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency enforces strict regulations for electronic prescriptions, including two-factor authentication that meets criteria for low “false match” rates. This is where biometrics are an ideal solution. According to Imprivata, a biometric security company that services the healthcare industry, fingerprint biometric identification has a false match rate of less than 0.1%.
Furthermore, biometric security can be used to accurately identify the patients that come in for treatment. Patient misidentification is a ubiquitous issue in healthcare facilities around the country, placing patients at risk of being permanently harmed by incorrect treatment. According to a 2016 study on patient identification errors by the ECRI Institute, 72.3% of identification errors occur during clinical encounters, such as when patients are being seen by doctors or undergoing operations or testing; 12.6% of errors occurred during patient intake. With the use of biometrics, nurses quickly can scan patients when they’re being registered or scheduled for care, and a doctor can perform a second scan when they meet the patient to make sure they’re seeing the correct patient.
Patients Still are Skeptical
Despite the positive benefits of biometric security technology, patients and providers still express skepticism about systems that store personal biometric data, like thumbprints and iris patterns. A 2018 study by the University of Texas reported that only 58% of respondents feel very comfortable with fingerprint recognition technology, while about 33% are comfortable with other forms of biometrics technology. Survey respondents were most unsure about facial recognition, with 13% feeling “not at all comfortable” with the technology.
The key to overcoming patient and provider skepticism about biometrics is education. Many of the concerns raised about biometrics-based security systems revolve around protecting the privacy of the stored biometric data. Patients and healthcare professionals must be educated on how biometric information is protected and unable to be shared with third parties or government organizations. As the public comes to understand biometrics better and the technology becomes more commonplace, public skepticism is likely to wane.
Aeris Provides Secure Networks for Healthcare IoT
The growth of the biometrics industry will continue at a fast pace, becoming more commonplace as it penetrates all levels of technology. Increased investment in healthcare biometrics will offer a safer and more secure healthcare network to both patients and professionals. With robust security and multi-factor authentication, patients can rest easy knowing that their private medical information is protected from prying eyes. And healthcare professionals can be assured that they not only have the right patient but also the necessary information to provide the proper treatment.
As electronic healthcare systems grow more robust and share secure information to professionals across the cloud, security measures will become even more important to protecting patients and their data. That’s why Aeris believes that IoT needs security at the design stage. We have developed the tools and expertise to mitigate risks with the responsible development of IoT applications for the healthcare industry. With our cloud-based Aeris Intelligent IoT Network, we make it easier than ever for companies to securely manage and optimize their IoT/M2M deployments.
To learn more about our IoT solutions for the healthcare industry, contact Aeris today.